Are you curious to learn about valve body manufacture? Look no further! This ultimate guide has you covered with everything you need to know. Whether you're a beginner dipping your toes into the world of valve bodies or an industry expert looking to deepen your knowledge, this comprehensive article will provide the insights you're seeking. In this guide, we will explore the intricacies of valve body manufacture, from the various types of valves and their applications to the manufacturing processes involved. We'll delve into the materials used, the importance of quality control, and the latest technological advancements shaping the industry. With a focus on accuracy and relevance, our goal is to equip you with the right information to make informed decisions. By the end of this guide, you'll have a solid understanding of the inner workings of valve body production and be better positioned to optimize your business operations or pursue new opportunities. So, let's dive in and discover the fascinating world of valve body manufacture together!
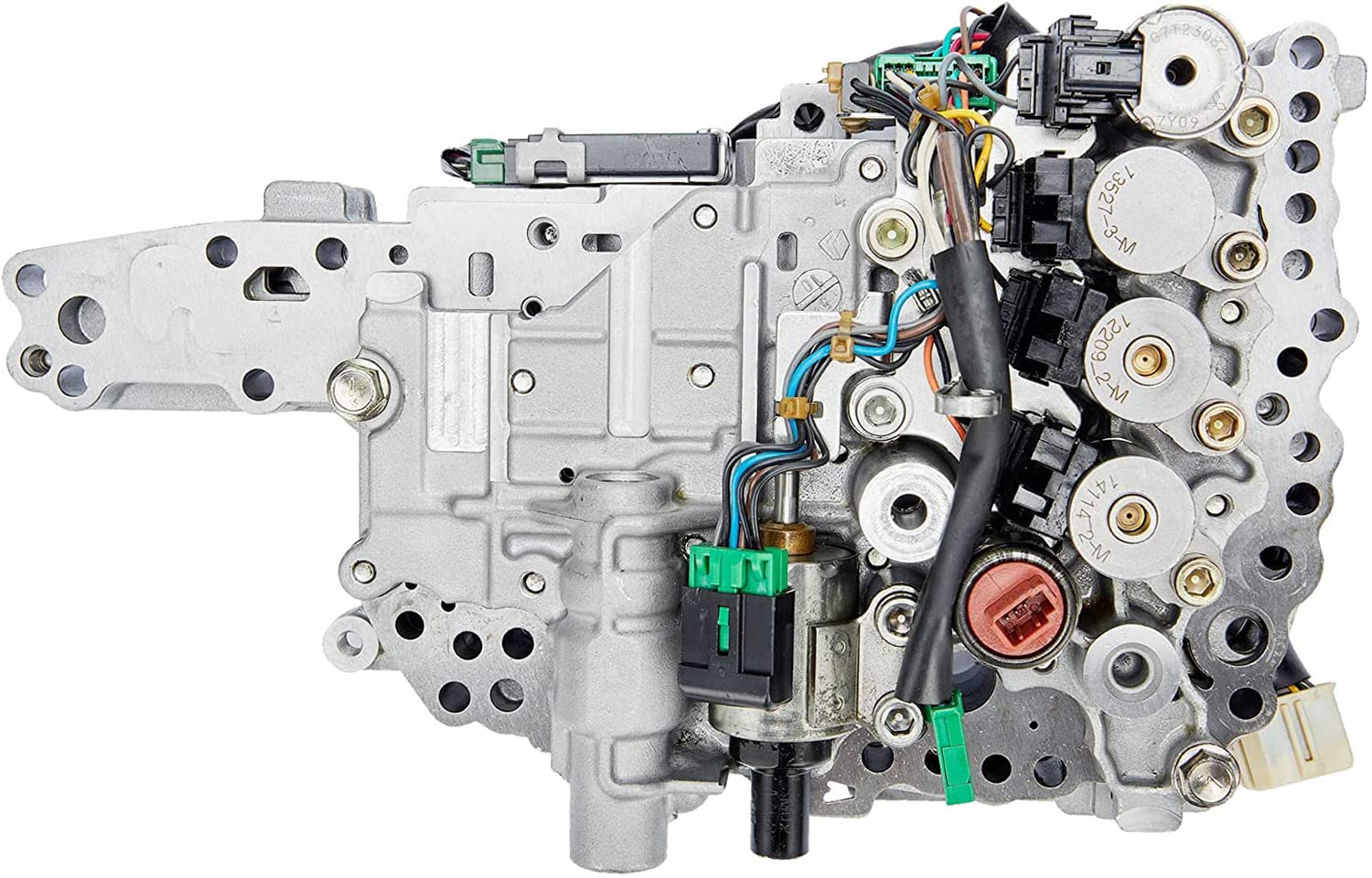
Importance of Valve Body in Mechanical Systems
Valve bodies are the unsung heroes of mechanical systems, playing a crucial role in controlling the flow of fluids and gases. Whether it's in your car's transmission, a hydraulic system, or your home's plumbing, valve bodies are integral to their proper functioning. These seemingly small components are responsible for regulating, directing, and managing the flow, pressure, and direction of fluids. Understanding the significance of valve bodies is essential for anyone who relies on machinery, from engineers and technicians to everyday consumers.
One of the primary reasons valve bodies are indispensable is their role in maintaining system efficiency. Imagine driving a car without a properly functioning transmission valve body. Shifting gears would become a chaotic and unpredictable experience. Similarly, in industrial settings, the failure of a valve body can lead to erratic fluid flow, compromising the efficiency and safety of operations. Thus, ensuring that valve bodies are well-maintained and of high quality is paramount.
Moreover, valve bodies are essential for safety. They prevent over-pressurization, which can result in catastrophic failures. In steam boilers, for instance, pressure relief valve bodies are designed to release excess pressure, preventing explosions. This is just one example of how valve bodies serve as a crucial line of defense against potential disasters.
In addition to safety and efficiency, valve bodies also contribute to the longevity of mechanical systems. When fluids or gases flow smoothly and as intended, wear and tear on other components are reduced. This extends the lifespan of machinery, ultimately saving money on repairs and replacements.
.jpg)
Components of a Valve Body
To truly understand the inner workings of valve bodies, it's essential to break down their components. Valve bodies are intricate assemblies comprising various elements, each with its own specific function. The core components of a typical valve body include:
-
Valve Housing: The outer shell of the valve body, often made of metal or high-strength plastic, provides structural support and protection to the internal components.
-
Valve Ports: These are the openings in the valve body through which fluids or gases flow. Ports can vary in size and shape depending on the application.
-
Valve Seats: These are the surfaces where the valve rests when closed, sealing off the flow of fluid or gas. Proper sealing is essential to prevent leaks.
-
Valve Disc or Ball: The movable component that opens or closes the valve by blocking or allowing the passage of fluid or gas. It's often designed to fit precisely into the valve seats for a tight seal.
-
Actuator: The mechanism responsible for moving the valve disc or ball. Actuators can be manual (operated by hand), pneumatic (using compressed air), hydraulic (using liquid pressure), or electric (controlled by an electrical signal).
-
Stem: The component that connects the actuator to the valve disc or ball, transmitting the force needed to open or close the valve.
-
Bonnet: A cover that encases the valve stem and provides a seal to prevent leaks.
-
Control Mechanism: In some cases, a valve body may have a control mechanism, such as a solenoid, that allows for remote or automated operation.
These components work in tandem to control the flow of fluids or gases, ensuring that it happens smoothly, efficiently, and as required by the system. The proper design and assembly of these components are critical to the valve body's overall performance.
.jpg)
Valve Body Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing of valve bodies is a precise and intricate process that demands a high degree of precision and quality control. Let's delve into the steps involved in creating these essential components:
-
Material Selection: The process begins with the careful selection of materials. The choice of material depends on the intended application, with common options including stainless steel, cast iron, brass, aluminum, and various plastics. Material selection is crucial as it determines the valve body's durability and resistance to corrosion.
-
Machining: Once the material is selected, it undergoes machining processes to shape it into the required components. This includes cutting, drilling, and shaping the valve housing, ports, seats, and other parts to precise specifications.
-
Assembly: Valve bodies are typically assembled by skilled technicians who ensure that all components fit together seamlessly. The valve disc or ball is carefully positioned, and the actuator and stem are attached. Special attention is given to achieving a perfect seal between the valve disc and seats.
-
Quality Control: Quality control measures are implemented at every stage of manufacturing. This includes rigorous inspections to check for dimensional accuracy, surface finish, and proper alignment of components. Pressure testing is often performed to verify that the valve body can withstand the intended operating conditions without leakage.
-
Surface Treatment: Depending on the material and application, valve bodies may undergo surface treatments such as plating or coating to enhance their corrosion resistance and durability.
-
Final Testing: Before leaving the manufacturing facility, valve bodies undergo comprehensive testing to ensure they function as designed. This includes functional tests to confirm that the valve opens and closes correctly and leakage tests to ensure there are no leaks under pressure.
-
Documentation: Detailed documentation, including specifications, test results, and material certifications, is typically provided with each valve body to assist with installation and maintenance.
The precision and care taken during the manufacturing process directly impact the performance and longevity of valve bodies. Quality manufacturing is essential to ensure that these components can reliably control fluid and gas flow in various applications.
Different Types of Valve Body
Valve bodies come in a wide variety of types and designs, each tailored to specific applications and industries. Understanding the different types is crucial for selecting the right valve body for a given task. Here are some common types of valve bodies:
-
Gate Valve Bodies: Gate valves feature a flat or wedge-shaped disc that moves perpendicular to the flow direction. They provide excellent shutoff capabilities and are often used in applications where a tight seal is essential.
-
Ball Valve Bodies: Ball valves use a spherical disc to control flow. They are known for their quick quarter-turn operation, making them ideal for applications where fast shutoff is required.
-
Butterfly Valve Bodies: Butterfly valves use a circular disc mounted on a shaft. Rotating the disc controls flow. They are compact and lightweight, making them suitable for large pipelines.
-
Check Valve Bodies: Check valves allow flow in one direction and prevent reverse flow. They are commonly used to prevent backflow in plumbing systems.
-
Diaphragm Valve Bodies: Diaphragm valves use a flexible diaphragm to control flow. They are often used in applications where contamination or leakage must be minimized.
-
Pressure Relief Valve Bodies: These valves automatically release excess pressure to prevent system over-pressurization. They are crucial for safety in many industrial processes.
-
Control Valve Bodies: Control valves are designed to precisely regulate flow, pressure, and temperature in industrial processes. They often include sophisticated control mechanisms and instrumentation.
-
Solenoid Valve Bodies: Solenoid valves are typically used in automated systems and rely on electrical signals to control flow. They are found in applications ranging from irrigation systems to industrial automation.
-
Needle Valve Bodies: Needle valves feature a long, tapered needle-like stem that allows for precise flow control. They are commonly used in laboratory equipment and precision instruments.
Each type of valve body has its own set of advantages and limitations. Selecting the right type involves considering factors such as the fluid or gas being controlled, pressure and temperature requirements, flow rates, and the need for shutoff capabilities. Proper selection ensures that the valve body performs optimally and prolongs the life of the mechanical system it serves.
.jpg)
Common Materials Used in Valve Body Manufacturing
The materials used in valve body manufacturing are diverse and carefully chosen to suit specific applications. The choice of material not only affects the valve body's durability but also its resistance to corrosion and compatibility with the fluids or gases it will handle. Here are some common materials used in valve body manufacturing:
-
Stainless Steel: Stainless steel is prized for its corrosion resistance and durability. It is widely used in industries where hygiene and resistance to chemical corrosion are essential, such as food processing and pharmaceuticals.
-
Cast Iron: Cast iron is known for its strength and reliability. It is often used in heavy-duty applications where robustness is required, such as water and wastewater systems.
-
Brass: Brass is valued for its malleability and excellent conductivity. It is commonly used in plumbing and HVAC systems.
-
Aluminum: Aluminum is lightweight and corrosion-resistant, making it suitable for applications where weight is a concern, such as aerospace and automotive.
-
Bronze: Bronze offers good corrosion resistance and is often chosen for marine and seawater applications.
-
Plastics: Various plastics, such as PVC, CPVC, and PTFE, are used for valve bodies in applications where chemical resistance, low cost, and lightweight properties are crucial.
-
Carbon Steel: Carbon steel provides strength and is commonly used in industrial settings for high-pressure applications.
The choice of material is influenced by factors such as the type of fluid or gas being controlled, the temperature and pressure conditions, and the specific requirements of the application. It's essential to select the appropriate material to ensure the valve body's longevity and performance.
In addition to the base material, valve bodies may undergo surface treatments or coatings to enhance their properties further. For instance, adding a layer of chrome or nickel can improve corrosion resistance, while coatings like Teflon can reduce friction and enhance sealing capabilities. The combination of material selection and surface treatments is a critical consideration in valve body manufacturing.
Quality Control in Valve Body Production
Maintaining the highest quality standards in valve body production is paramount to ensure their reliability and performance. Quality control measures are integrated throughout the manufacturing process to identify and rectify any defects or deviations from specifications. Here are some key aspects of quality control in valve body production:
-
Dimensional Accuracy: Precise machining and assembly are essential to ensure that valve bodies meet the specified dimensions. Any deviations can lead to improper fitment and potential leakage.
-
Surface Finish: The surface finish of valve bodies is critical to their performance. Rough surfaces can lead to increased friction and wear. Quality control checks ensure that surfaces are smooth and free from defects.
-
Pressure Testing: Valve bodies must be able to withstand the pressures they are designed for without leaking. Pressure testing is conducted to verify the integrity of the valve body under various conditions.
-
Leakage Testing: Specialized tests are performed to detect any leaks in valve bodies. This includes both internal and external leakage checks to ensure that fluids or gases do not escape when the valve is closed.
-
Material Verification: Material certifications and inspections are conducted to confirm that the chosen material meets the required standards and specifications.
-
Tightness of Seals: Ensuring that valve discs or balls create a tight seal with valve seats is critical. This prevents unwanted leaks and ensures proper control of fluid or gas flow.
-
Functional Testing: Valve bodies undergo functional testing to verify that they operate as intended. This includes checks of the actuator's movement, the responsiveness of the valve, and the ease of operation.
-
Documentation: Comprehensive documentation is maintained throughout the manufacturing process, detailing the materials used, inspections performed, and test results. This documentation is vital for traceability and quality assurance.
Quality control is not a one-time process but a continuous effort that begins with material selection and extends through every stage of manufacturing. It is a collaborative effort involving engineers, technicians, and quality control specialists to ensure that each valve body leaving the production facility meets the highest standards of quality and reliability.
Choosing the Right Valve Body Manufacturer
Selecting the right valve body manufacturer is a critical decision that can impact the performance and reliability of your mechanical systems. Whether you are an engineer sourcing components for an industrial application or a homeowner in need of plumbing fixtures, here are key considerations to guide your choice:
-
Reputation and Experience: Look for manufacturers with a strong reputation and a track record of producing high-quality valve bodies. Experience often translates to expertise in design, manufacturing, and quality control.
-
Certifications: Check if the manufacturer adheres to industry standards and holds relevant certifications. ISO 9001 certification, for example, demonstrates a commitment to quality management.
-
Materials Expertise: Ensure that the manufacturer is well-versed in working with the materials suitable for your application. Different materials have unique properties and requirements.
-
Customization Capability: If your project requires specialized valve bodies, inquire about the manufacturer's ability to customize designs to meet your specific needs.
-
Quality Control Processes: Investigate the manufacturer's quality control processes to ensure they align with your expectations for quality and reliability.
-
Lead Times and Delivery: Consider production lead times and delivery schedules to ensure that your project timeline can be met.
-
Support and Service: Evaluate the manufacturer's commitment to customer support and after-sales service. Quick and responsive support can be invaluable in case of issues or maintenance needs.
-
Cost and Value: While cost is a consideration, prioritize value over price. High-quality valve bodies may have a higher upfront cost but can lead to long-term savings through reduced maintenance and improved system performance.
-
References and Reviews: Seek references from other clients who have worked with the manufacturer and read reviews or testimonials to gauge customer satisfaction.
-
Environmental Practices: If environmental sustainability is a concern, inquire about the manufacturer's environmental practices, including recycling and waste management.
Taking the time to research and select the right valve body manufacturer is an investment in the performance and reliability of your mechanical systems. It can also contribute to cost savings and peace of mind, knowing that you have chosen a trusted partner in your project.
.jpg)
Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Valve Bodies
Proper maintenance and troubleshooting of valve bodies are essential to ensure their long-term performance and prevent costly downtime. Whether you're responsible for an industrial plant's valve systems or the plumbing in your home, here are some key maintenance and troubleshooting tips:
Maintenance:
-
Regular Inspection: Periodically inspect valve bodies for signs of wear, corrosion, or leakage. Catching issues early can prevent more significant problems.
-
Lubrication: Some valve bodies require periodic lubrication to maintain smooth operation. Check manufacturer guidelines for lubrication intervals and appropriate lubricants.
-
Seal Replacement: If you notice leaks around the valve, consider replacing seals or gaskets. Proper sealing is crucial for preventing leaks.
-
Cleaning: In environments with debris or contaminants, keep valve bodies clean. Foreign particles can interfere with proper valve operation.
-
Actuator Maintenance: If your valve body has an actuator, ensure it operates smoothly and responds correctly to control signals. Lubricate and inspect actuators as needed.
-
Pressure Testing: Periodically conduct pressure tests to verify that the valve body can withstand the specified pressures without leaking.
-
Temperature Monitoring: In high-temperature applications, monitor the valve body's temperature to ensure it stays within safe limits. Excessive heat can degrade seals and materials.
-
Documentation: Maintain records of maintenance activities, including dates, repairs performed, and any issues encountered. This documentation aids in tracking the valve body's history.
Troubleshooting:
-
Leakage: If you notice leaks, start by inspecting seals, gaskets, and the valve disc or ball for damage or wear. Tightening connections may resolve minor leaks.
-
Sticking or Binding: If the valve body is difficult to operate or sticks in position, check for obstructions, debris, or corrosion in the valve housing. Cleaning and lubrication may help.
-
Inadequate Flow: If the valve is not allowing the desired flow, verify that it is fully open and that there are no obstructions in the line. Check for damage to the valve disc or ball.
-
Actuator Issues: If the actuator fails to respond or behaves erratically, inspect the electrical or hydraulic connections, control signals, and power sources.
-
Excessive Noise or Vibration: Unusual noise or vibration can indicate problems with the valve body or associated components. Investigate the source of the noise and address it promptly.
-
Corrosion: Corrosion can weaken valve bodies over time. If you notice signs of corrosion, consult with a professional for recommendations on repair or replacement.
-
Temperature and Pressure Fluctuations: Sudden fluctuations in temperature or pressure can stress valve bodies. Ensure that the system is operating within specified limits to prevent damage.
-
Professional Inspection: For complex issues or when in doubt, consider engaging a qualified technician or engineer to assess and troubleshoot valve body problems.
Regular maintenance and prompt troubleshooting can extend the life of valve bodies and ensure that they continue to function reliably. Neglecting maintenance can lead to costly repairs and system downtime, making proactive care a wise investment.
Conclusion
Valve bodies are the unsung heroes of mechanical systems, playing a pivotal role in controlling the flow of fluids and gases across various applications. Understanding their importance, components, manufacturing processes, materials, and the need for quality control is crucial for anyone involved in mechanical systems, from engineers to consumers.
Choosing the right valve body manufacturer is a decision that should be made with care, considering factors such as reputation, materials expertise, customization capabilities, and quality control processes. The right manufacturer can be a trusted partner in ensuring the reliability of your mechanical systems.
Additionally, proper maintenance and troubleshooting practices are essential for the longevity and performance of valve bodies. Regular inspections, lubrication, and proactive problem-solving can prevent costly downtime and repairs.
In conclusion, valve bodies may be small components, but their impact on the efficiency, safety, and longevity of mechanical systems cannot be overstated. With the knowledge and considerations outlined in this guide, you can make informed decisions about valve bodies and their role in your specific applications.
.jpg)
FAQ 1: What Are the Key Advantages of Valve Body in Mechanical Systems?
Valve bodies are crucial components in various mechanical systems. They offer numerous advantages, including efficient fluid or gas flow control, enhanced safety through pressure regulation, and prolonged system lifespan due to reduced wear and tear. These advantages are particularly valuable in industries like automotive, manufacturing, and oil and gas. By ensuring optimal performance, valve bodies contribute to system efficiency, cost savings, and safety compliance.
FAQ 2: Can You Explain the Different Types of Valve Bodies and Their Applications?
Certainly! Valve bodies come in diverse types tailored to specific applications. Gate valves provide tight shutoff and are ideal for applications requiring isolation. Ball valves are known for their quick operation and find use in applications needing rapid shutoff. Butterfly valves are compact and versatile, while check valves prevent reverse flow. Diaphragm valves minimize contamination risks, and pressure relief valves ensure safety. Control valves, solenoid valves, and needle valves cater to precise flow control needs. Each type serves a unique purpose, making selection crucial for optimal system performance.
FAQ 3: Which Materials Are Typically Used in Valve Body Manufacturing, and How Does Material Choice Impact Performance?
Valve bodies are manufactured using various materials, such as stainless steel, cast iron, brass, aluminum, bronze, and plastics, each chosen to match specific applications. Stainless steel offers exceptional corrosion resistance, while cast iron provides strength. Brass and aluminum excel in plumbing and HVAC systems, and bronze is favored for marine applications. Material choice significantly affects the valve body's durability, resistance to corrosion, and compatibility with handled fluids or gases. Proper material selection ensures peak performance and longevity.
FAQ 4: How Does Quality Control Play a Role in Ensuring Reliable Valve Body Production?
Quality control is integral to valve body manufacturing. It involves meticulous inspections, including dimensional accuracy checks, surface finish assessments, and pressure and leakage tests. Material verification and tightness of seals are essential. Comprehensive documentation accompanies each valve body, detailing specifications and test results. Quality control measures ensure that valve bodies meet rigorous standards, guaranteeing reliability and safety in various applications, from industrial plants to residential plumbing systems.
FAQ 5: What Should We Consider When Choosing a Valve Body Manufacturer, and How Can We Verify Their Expertise?
When selecting a valve body manufacturer, consider their reputation, experience, certifications, and materials expertise. Research reviews and testimonials to gauge customer satisfaction. Assess customization capabilities, adherence to industry standards like ISO 9001, and commitment to environmental practices. Review lead times, support services, and overall value, prioritizing quality over price. A reliable valve body manufacturer should have a strong track record and a commitment to quality, ensuring the success and longevity of your mechanical systems.